CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY (CARDIAC CATHETERISATION)

Dr. Richard Mansfield
BSc (Hons) MB ChB MD FRCP FESC
CONSULTANT CARDIOLOGIST
![]()
Note: I am happy to answer general questions regarding the content of this website, but I cannot give clinical advice. Such requests will not be answered.
An echocardiogram is a safe and comfortable test, which uses ultrasound to acquire images of the heart. This is the same technology that is used to scan pregnant women.
A probe is placed on the front of the chest with some jelly to enhance the signal and a number of pictures are taken of the heart with the patient laid on a couch on their left side. This allows the operator to look at the over-all pump function of the heart and to see whether or not any of the cardiac chambers are enlarged. It also allows detailed analysis of the heart valves.
 Echocardiogram - This is a sophisticated ultrasound machine that can provide detailed information about the heart. It is safe and not uncomfortable.
Echocardiogram - This is a sophisticated ultrasound machine that can provide detailed information about the heart. It is safe and not uncomfortable.
JPEG (41 kb)
 Echocardiography Room
Echocardiography Room
JPEG (28 kb)
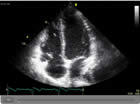 Echocardiogram 1 - This is an ultrasound image showing all four chambers of the heart.
Echocardiogram 1 - This is an ultrasound image showing all four chambers of the heart.
Flash video (162 kb)
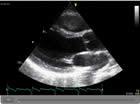 Echocardiogram 2 - This ultrasound image shows the aortic and mitral valves as well as the main heart chambers.
Echocardiogram 2 - This ultrasound image shows the aortic and mitral valves as well as the main heart chambers.
Flash video (185 kb)
Flash videos require Adobe Flash Player.
Download Adobe Flash Player
This test combines an echocardiogram with either exercise or an infusion of a drug to put the heart under some additional strain. By looking at the function of the heart muscle in this way it may be possible to see if there is a problem with blood flow. It is a useful alternative for those patients who cannot manage an exercise treadmill test and to investigate chest pain/angina.
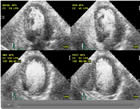 Stress Echocardiogram
Stress Echocardiogram
Flash video (95 kb)
Flash videos require Adobe Flash Player.
Download Adobe Flash Player
This investigation is used to look at 'holes in the heart' called patent foramen ovale or atrial septal defects. A small amount of salt solution is mixed with the patient's blood to create a froth, which is injected into a vein. An echocardiogram is then performed to see if any of the tiny bubbles in the froth pass in an unusual direction through the heart. Although it may seem like a strange test it is perfectly safe!
It is occasionally necessary to gain some further detail of the heart using ultrasound and requires the placement of a fine probe in the gullet under sedation. Sedation is administered through a small tube (cannula) placed in the back of the hand. It is carried out as a day case procedure and patients need to starve for 4 hours beforehand. This is a particularly good test for looking at specific valve disease and other cardiac conditions.
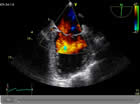 Transoesophageal Echocardiogram (TOE)
Transoesophageal Echocardiogram (TOE)
Flash video (93 kb)
Flash videos require Adobe Flash Player.
Download Adobe Flash Player